
Characteristics and Different Shaped Colony of Bacteria and Mold Growing on Agar Plates . Stock
Yeast and Mold Agar should be sterilized without pH adjustment and sterile acid added to the medium cooled to 45 - 50°C. Acidified Yeast and Mold Agar should not be heated.. Plates per 500 g: 670.00 Preparation: Suspend 41 grams of the medium in one liter of purified water. Heat with frequent agitation and boil for one minute to completely.
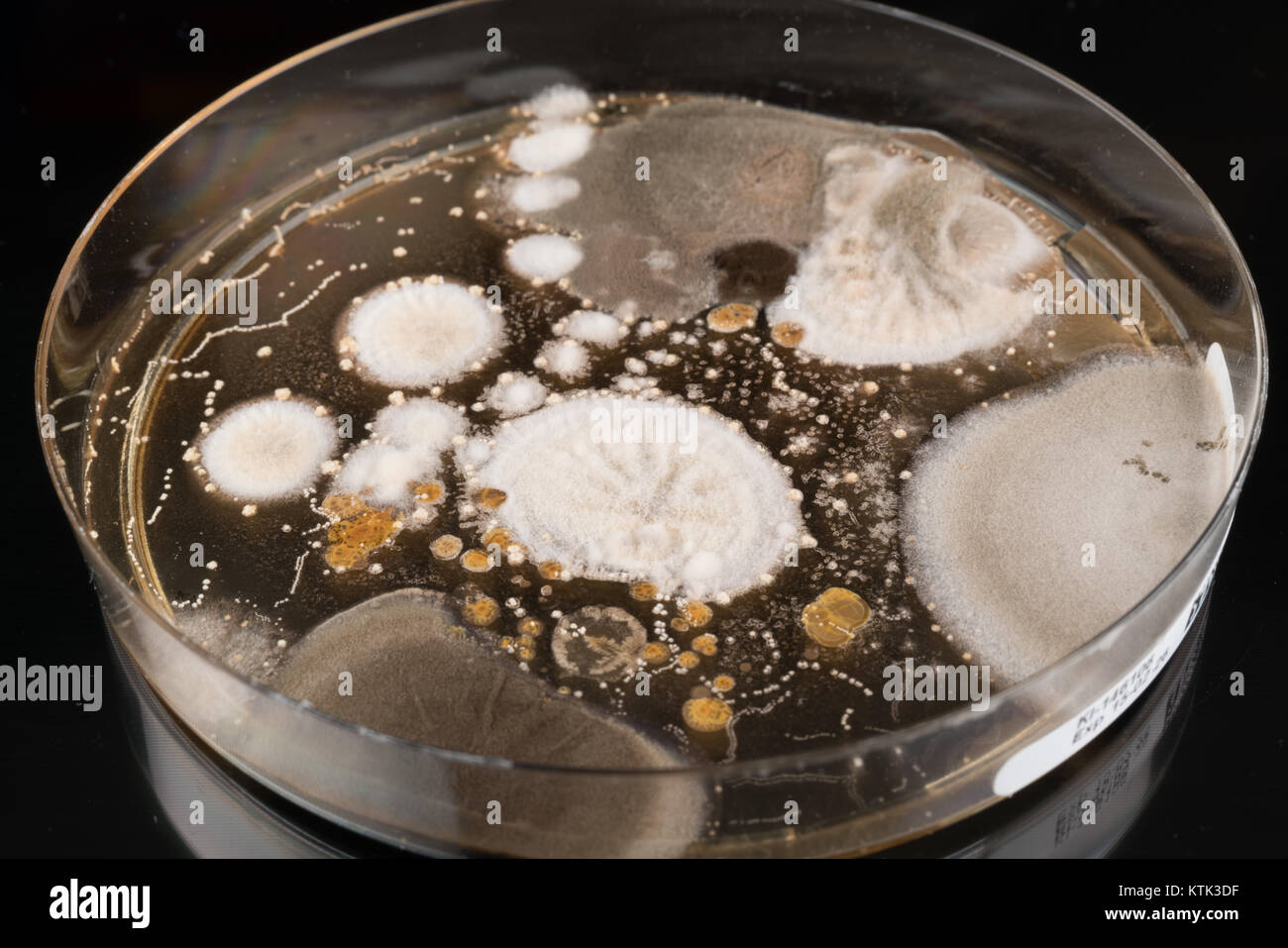
growth of in a Petri dish, Bacteria, yeast and mold growing on an agar plate
Remove lid from test plate and set aside. Gently tap the item you wish to test with the plate 1-2 times. Make sure that the agar material is exposed to the item being tested when tapping. The puffs of air created from the tapping motion will cause any mold spores embedded in the item to attach to the agar material. Place lid back on test plate.
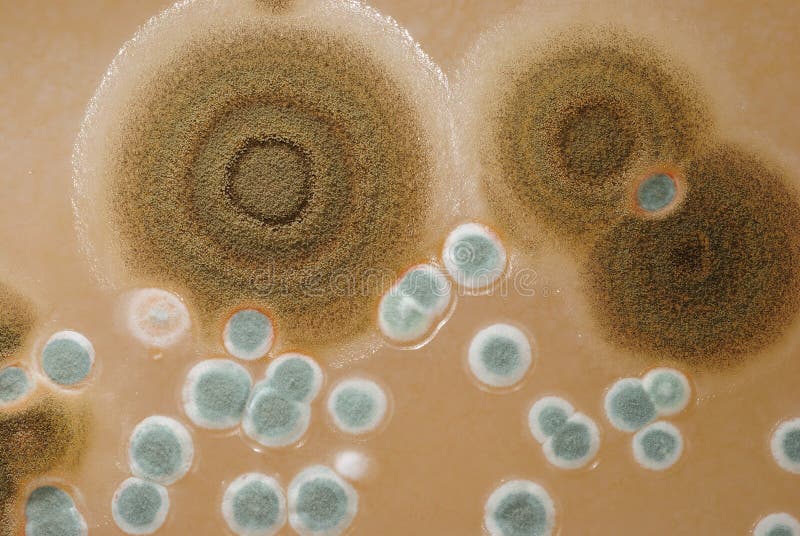
Macro Mold Colonies Growing On An Agar Plates. Stock Photo Image of biotechnology, antibiotic
If one is interested in testing for mold, agar plates containing malt extract agar (MEA) supplemented with some antibiotics to suppress bacterial growth would be used. The agar plates are left open at table-top level at selected points in the room for half-hour to 4 hours. This allows mold spores and fragments to settle onto agar media by gravity.
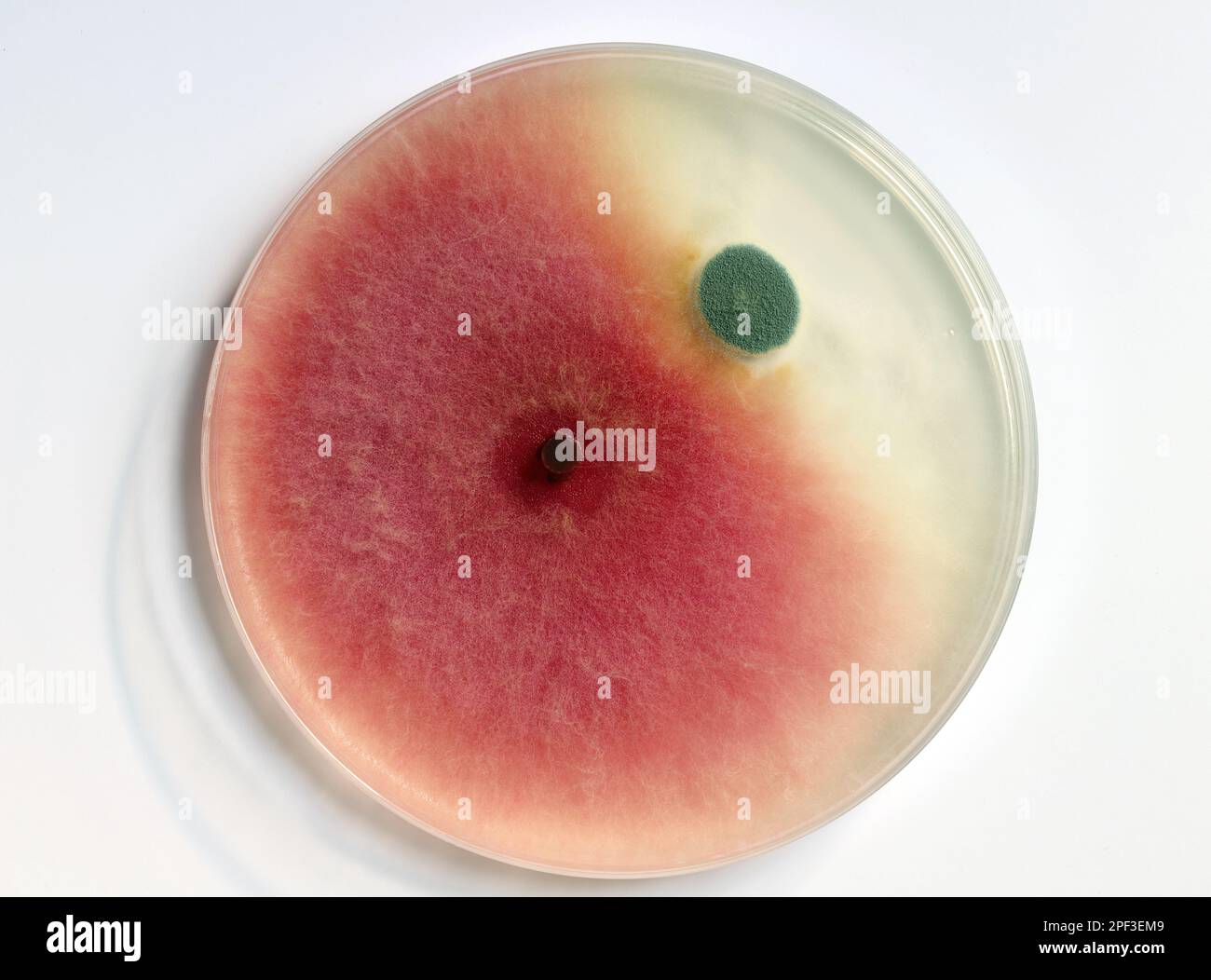
Culture of mold growing in a petri dish on a PDA, agar nutrient plate, colonies of Fusarium (red
Remove the parafilm seal and raise lids to expose the surface of the medium, rest the lid on the very edge of the plate so that the entire agar surface is completely exposed (see figure 1 on page 2). Take care not to put fingers on plates. Leave plates exposed for half an hour to 4 hours (4 hours recommended where there is no visible mould growth).

Characteristics and Different Shaped Colony of Bacteria and Mold Growing on Agar Plates . Stock
Hi guys! I could use Reddit's help in visually identifying the species of the mold growing on the three agar plates in the attached picture. The plates are Sabouraud's Dextrose Agar.

a mold colony on an agar plate (aspergillus niger Stock Photo Alamy
The 3M™ Petrifilm® Rapid Yeast and Mold Count Plate method is faster and provides results in as little as 48 hours of incubation time, vs. the traditional agar method that requires a five day incubation period. This plate features a new indicator technology that makes colonies easier to interpret.

Mildew Culture On Agar Plate Laboratory Scene HighRes Stock Photo Getty Images
Place loop or wire material portion of "fungus" colony onto slide with a drop of stain, and add a coverslip. Gently press down to flatten potential mold and agar. Use a paper towel dipped into alcohol for pressing. Discard towel and wipe hands with disinfectant and dry.

Mold Colonies Growing On An Agar Plates. Stock Photo 36073933 Shutterstock
Colony morphology is a method that scientists use to describe the characteristics of an individual colony of fungi growing on agar in a Petri dish. It can be used to help to identify them. Colony morphology. A circular piece of bread that has been allowed to go mouldy. Plate 1 contains a circular piece of bread that has been allowed to go mouldy.

growth of in a Petri dish, Bacteria, yeast and mold growing on an agar plate
Label with the location, time, and date if testing. Open the plate and set it on a flat surface with the lid face down beside it. Leave the plate open for one hour. After an hour close the plate up and seal it. Stickers are included to seal the plates. Place the plates in the foil bag in a dark location for 5-7 days.

Macro Mold Colonies Growing On An Agar Plates. Stock Photo Image 20410960
Petri dishes (also called settling plates) are designed to grow mold spores and since there are mold spores in the air everywhere all the time, you should expect to get mold spores growing on the plates. But since plates can only capture a limited group of spores (i.e., the ones closest to the plate and the heaviest ones that are more likely to.
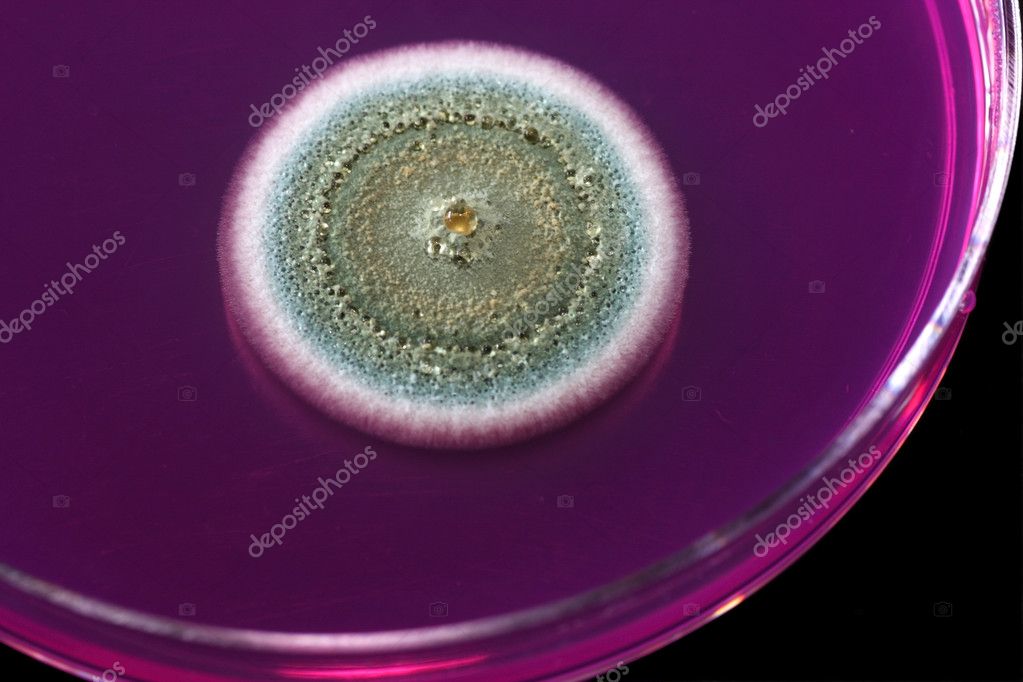
Mold on agar plate — Stock Photo © ggw1962 8606758
Wash & dry your hands thoroughly prior to testing. Hold the plate so the yellow agar is facing towards the object or pet. Tap the object in 4 different representative places (The yellow agar should not touch the object). This will force the mold spores into the air and onto the plate. How-To Sample: Visible Mold.

Characteristics and Different Shaped Colony of Bacteria and Mold Growing on Agar Plates from
Plate count agar (PCA), standard methods. DG18 agar is used as a general purpose mold enumeration medium and is preferred when the a w of the analyzed food is less than 0.95. The low water.

Characteristics and Different Shaped Colony of Bacteria and Mold Growing on Agar Plates . Stock
Yeast and Mold Count Plates identify food borne yeast and mold in your food products and in your food processing environment. Yeasts are easily differentiated from molds on the plate: - Yeasts are typically indicated by small, blue-green colonies with defined edges and no foci. - Molds are…. Compare this item.

Macro Mold Growing On Agar Plate Stock Photo 66117334 Shutterstock
Wash & dry your hands thoroughly prior to testing. Hold the plate so the yellow agar is facing towards the object or pet. Tap the object in 4 different representative places (The yellow agar should not touch the object). This will force the mold spores into the air and onto the plate. How-To Sample: Visible Mold.

Characteristics and Different Shaped Colony of Bacteria and Mold Growing on Agar Plates . Stock
What Can Grow on a Nutrient Agar Plate? Bacteria. Each distinct circular colony should represent an individual bacterial cell or group that has divided repeatedly. Being kept in one place, the resulting cells have accumulated to form a visible patch. Most bacterial colonies appear white, cream, or yellow in color, and fairly circular in shape.
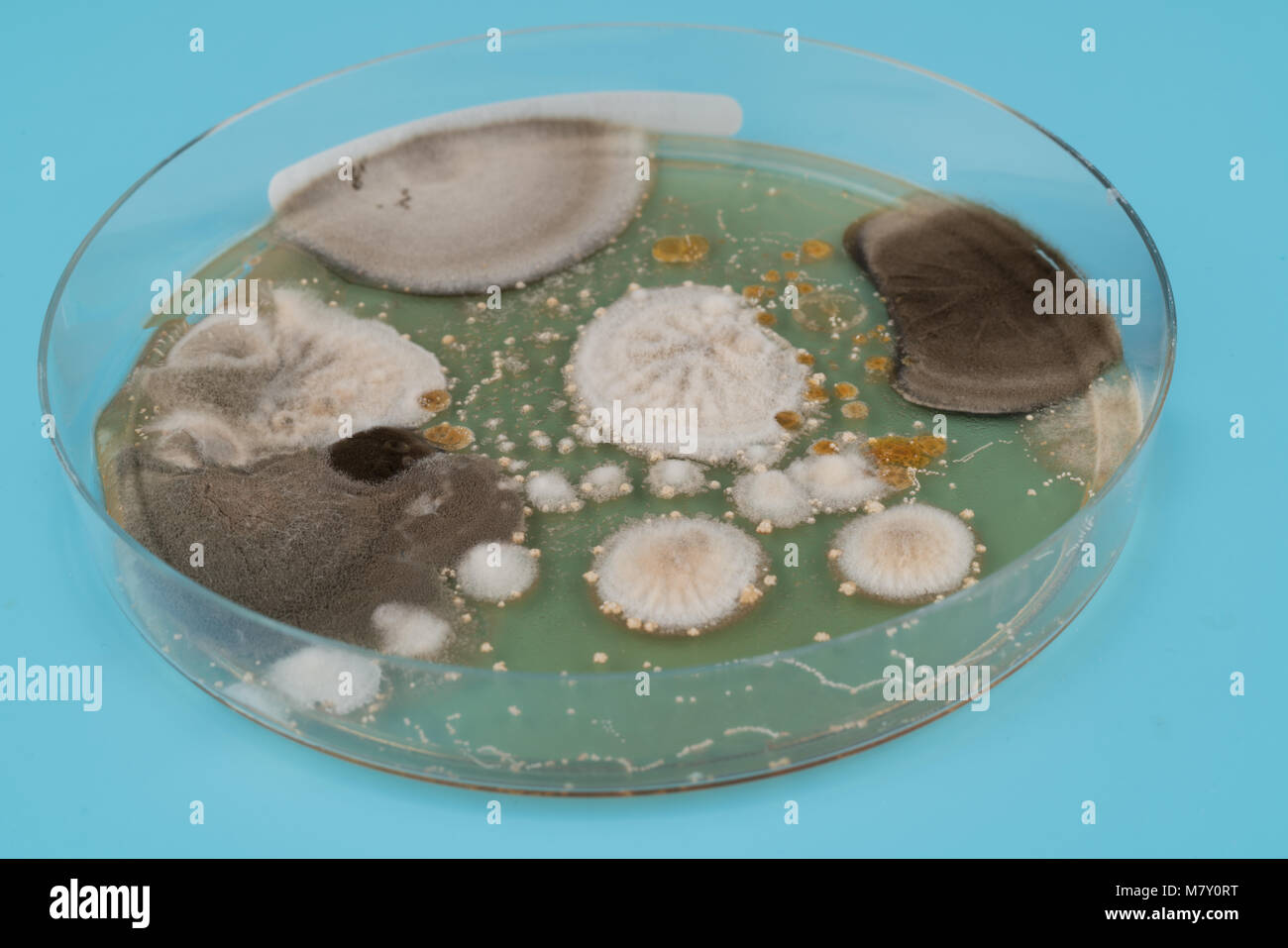

growth of in a Petri dish, Bacteria, yeast and mold growing on an agar plate
Ready-to-use Potato Dextrose Agar Plates are a general purpose medium for the cultivation of fungi, including yeasts and molds. It is used for pharmaceutical product sterility tests according to the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and for plate count enumeration tests for dairy products, foods, and…. Compare this item.